Stem cells: new insights for future regenerative medicine approaches
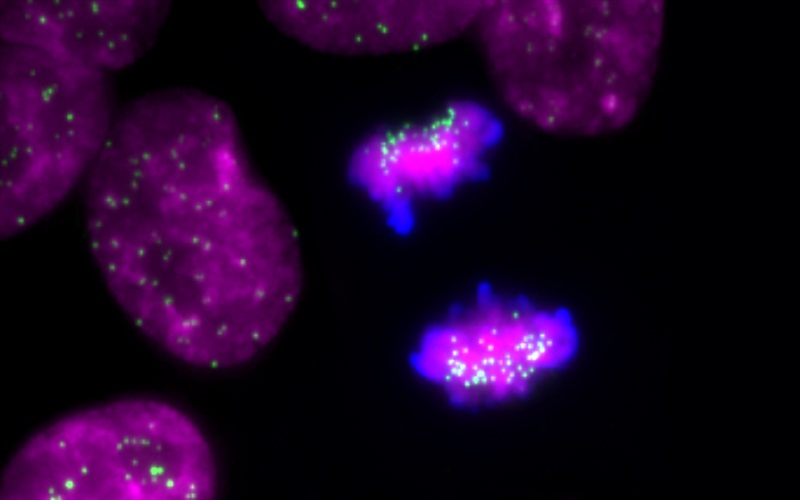
Researchers discover that a specialized part of the chromosomes, essential for a correct cell division, is smaller and weaker in stem cells, when compared to the ones of differentiated cells. The study published in Open Biology unravels important data for a better understanding of the process of division in stem cells and for the development of safer ways to use them in medicine.
Stem cells are considered one of the most promising tools in the field of regenerative medicine because they are a cell type that can give rise to all the cells in our bodies and that has the potential to be used to treat tissue loss due to damage or disease. Despite their potential, little is known about the mechanisms that govern the division of stem cells, which have propensity to accumulate chromosome segregation errors during this process. Stem cells can duplicate almost indefinitely and one of the elements necessary for a successful cell division (or mitosis) is the centromere.
Driven by the curiosity to understand the mechanisms that govern chromosome segregation in stem cells, the team of researchers from the IGC, led by Raquel Oliveira and Lars Jansen, designed a fundamental biology project with eyes set on centromeres and the protein complexes associated to them. The study allowed “a precise definition of the composition and size of the centromeres of stem cells and revealed that their chromosomes have weaker centromeres when compared to the ones of differentiated cells. Moreover, these structures become weaker as a consequence of acquiring the identity of stem cell itself”, explains Inês Milagre, main author of the study. “This ‘weakness’ in a structure of such importance for the correct distribution of chromosomes between daughter-cells might explain why these cells make more mistakes when they divide”, adds Lars Jansen, principal investigator at the IGC and the University of Oxford.
The high tendency for errors during cell division, which originates chromosomal anomalies, is currently one of the biggest limitations to the usage of these cells. “To overcome this limitation we must understand why such mistakes occur. Beyond the important discovery of this study, we are now looking at other structures that are important for cell division in order to have a more holistic vision of all the mitotic machinery of stem cells, so that we can revert their tendency for erroneous divisions”, reveals Raquel Oliveira, principal investigator at IGC. This study brings new perspectives to the understanding of cell division fidelity and points our possible causes for the presence of anomalies, which can greatly impact the therapies developed in the field of regenerative medicine.
Read Press Release
Read Paper
